
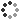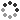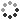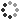
Comet Siding Spring streaking across the sky, as seen by NASA's Wide-field Infrared Survey Explorer, or WISE. This movie stitches together five frames taken by WISE as it orbited Earth during its ongoing infrared survey of the whole sky. The images span about eight hours of time. The comet, also known as C/2007 Q3, was discovered in 2007 by observers in Australia. The snowball-like mass of ice and dust spent billions of years orbiting in the deep freeze of the Oort Cloud, a spherical cloud of comets surrounding our solar system. At some point, it got knocked out of this orbit and onto a course that brings it closer to the sun. Sunlight has warmed the comet, causing it to shed ices and dust in a long tail that trails behind it. On October 7, 2009, comet Siding Spring passed as close as 1.2 astronomical units from Earth and 2.25 astronomical units from the sun (an astronomical unit is the distance between the sun and Earth). Now, the comet is leaving the warmer, more hospitable neighborhood of the solar system and heading back out to chillier parts.In this view, longer wavelengths of infrared light are red and shorter wavelengths are blue. The comet appears red because it is more than ten times colder than the surrounding stars. Colder objects give off more of their light at longer wavelengths. An ice cube, for example, pours out a larger fraction of its light at longer infrared wavelengths than a cup of hot tea emits.
| px | px | dpi | = | cm | x | cm | = | MB |
Details
Creative#:
TOP22312221
Source:
達志影像
Authorization Type:
RM
Release Information:
須由TPG 完整授權
Model Release:
N/A
Property Release:
No
Right to Privacy:
No
Same folder images:
 Loading
Loading