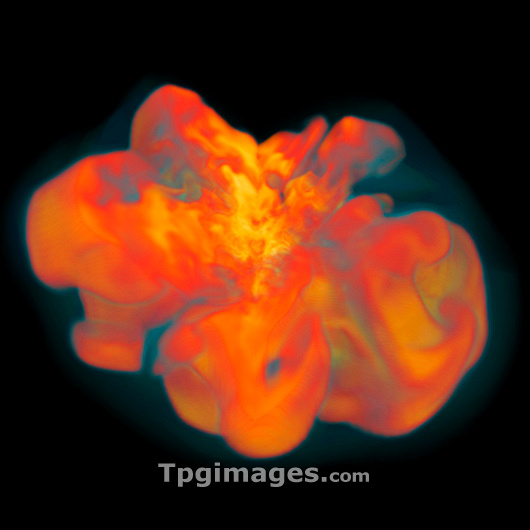
Supernova explosion. Image 4 of 4. Supercomputer simulation showing a supernova explosion 500 milliseconds (thousandths of a second) after core collapse. Supernovae occur when a massive star has run out of nuclear fuel and its core collapses to form a neutron star. The collapsed core triggers a shock wave that powers the supernova explosion. This simulation shows the entropy (amount of disorder in a thermodynamic system) of matter (light areas) that is rising due to heating by neutrinos at the core (unseen). The heated matter rises and mixes with in-falling cold matter (dark areas) resulting in turbulence. It is thought that neutrino-driven convection energy accompanies the shock wave to power the supernova explosion. Simulation created at the Max Planck Institute for Astrophysics, Germany. For complete sequence, see images: R730/098 - R730/101.
| px | px | dpi | = | cm | x | cm | = | MB |
Details
Creative#:
TOP03224934
Source:
達志影像
Authorization Type:
RM
Release Information:
須由TPG 完整授權
Model Release:
N/A
Property Release:
N/A
Right to Privacy:
No
Same folder images:
 Loading
Loading