
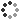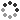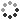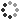
Coloured scanning electron micrograph (SEM) of activated and partially activated platelets, and a red blood cell. Red blood cells (RBCs, erythrocytes) take up oxygen from the lungs and distribute it around the body. Platelets are cell fragments in the blood that play an essential role in blood clotting and wound repair. They can also activate certain immune responses. Platelets are formed in the red bone marrow, lungs, and spleen by fragmentation of very large cells known as megakaryocytes. In the blood they are small oval disks termed nonactivated platelets or thrombocytes. Platelets serve as the body's first line of defence to prevent excessive blood loss. When an injury such as a cut is sustained, platelets change their shape (now known as activated platelets), become sticky and build up on a vessel wall to form a plug. They are also involved in the secretion of chemical platelet factors which help produce threads of fibrin. Blood cells collect in the entangled fibrin and platelet mass forming a blood clot at the site. Magnification: x1,600 when shortest axis printed at 25 millimetres.
| px | px | dpi | = | cm | x | cm | = | MB |
Details
Creative#:
TOP25525820
Source:
達志影像
Authorization Type:
RM
Release Information:
須由TPG 完整授權
Model Release:
N/A
Property Release:
N/A
Right to Privacy:
No
Same folder images:
 Loading
Loading